Every business needs to process customer orders efficiently and get paid for them in a timely way. The order-to-cash cycle comprises all the steps that make that happen, from order placement to payment. A streamlined, automated order-to-cash cycle can deliver a range of benefits, including better cash flow and happier customers. Here’s a deep dive into the steps in the order-to-cash cycle, a review of best practices, and a guide to automating the process.
What Is Order-to-Cash (OTC or O2C)?
Order-to-cash, commonly abbreviated as OTC or O2C, refers to all the steps involved in processing customer orders from the moment a customer places the order to when payment is received and applied to accounts receivable. Steps in the order-to-cash cycle include order management, order fulfillment, billing, payment processing, and reporting. A fast and efficient O2C cycle is critical for maintaining healthy cash flow because it reduces the time between receiving orders and getting paid. It also can boost revenue by ensuring that customers’ bills don’t slip through the cracks and go unpaid.
Order-to-Cash vs. Quote-to-Cash
While order-to-cash focuses on order processing and payment, quote-to-cash (QTC or Q2C) describes a broader set of steps used by companies offering goods or services that have variable pricing. Businesses that provide configurable products or project-based services often have a quote-to-cash process. Quote-to-cash adds several initial steps, such as quote preparation, to the order-to-cash process. These steps include configuring an offering to meet a customer’s needs, creating and presenting a quote, and negotiating pricing or other aspects of the offering. Once final terms are set and the customer places the order, the company then completes the rest of the order-to-cash cycle.
Key Takeaways
- The order-to-cash process includes all the steps from when a customer places an order to when the company receives payment.
- Steps in the order-to-cash cycle include order management and fulfillment, invoicing, payment, and reporting.
- Improvements to the order-to-cash process can accelerate cash flow, boost revenue, increase customer satisfaction, and improve operational efficiency.
- The order-to-cash cycle can be automated with an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system that integrates data from across the organization.
Order-to-Cash Explained
An efficient and automated order-to-cash cycle can improve cash flow—a critical concern for any business—while enhancing the customer experience. Accelerating the O2C process helps companies receive payment faster because they can process orders more quickly and invoice customers sooner. Creating an efficient O2C process requires integrating functions and data across different parts of the business, from order management and shipping to accounts receivable.
Because the order-to-cash process is one of the primary ways that a customer interacts with a business, it plays an important role in customer satisfaction. Customers should be able to place orders easily, understand exactly how much they owe and when their payment is due, and see when their order will be delivered. An efficient O2C cycle also helps ensure that customers quickly receive the goods they order. In contrast, slow or disorganized O2C processes can create problems that hurt the customer experience, such as shipping delays and inaccurate bills.
Why Is Order-to-Cash Important?
The order-to-cash process directly impacts a company's financial health and customer relationships. By reducing the time between order placement and payment collection, businesses bring in funds they can put towards other uses, such as covering current obligations or investing into growth initiatives. When this process is delayed, often due to manual processes in order fulfillment and invoice generation, it slows down deliveries and payments.
From an operational perspective, an effective order-to-cash process helps businesses better manage inventory, reduce processing costs, and make decisions based on accurate and up-to-date financial data rather than assumptions about when and if customers will pay. To gain this visibility, companies can integrate data across different stages of the O2C cycle and calculate key metrics, such as days sales outstanding (DSO) and order processing time. These insights help business leaders identify bottlenecks and reduce operational inefficiencies, in turn offering customers faster deliveries and more accurate invoices.
What Is the Order-to-Cash Process?
An efficient order-to-cash cycle makes sure that all orders are processed, fulfilled, invoiced, and paid as swiftly as possible. It should also aim to optimize the customer’s experience, from ordering to delivery and payment.
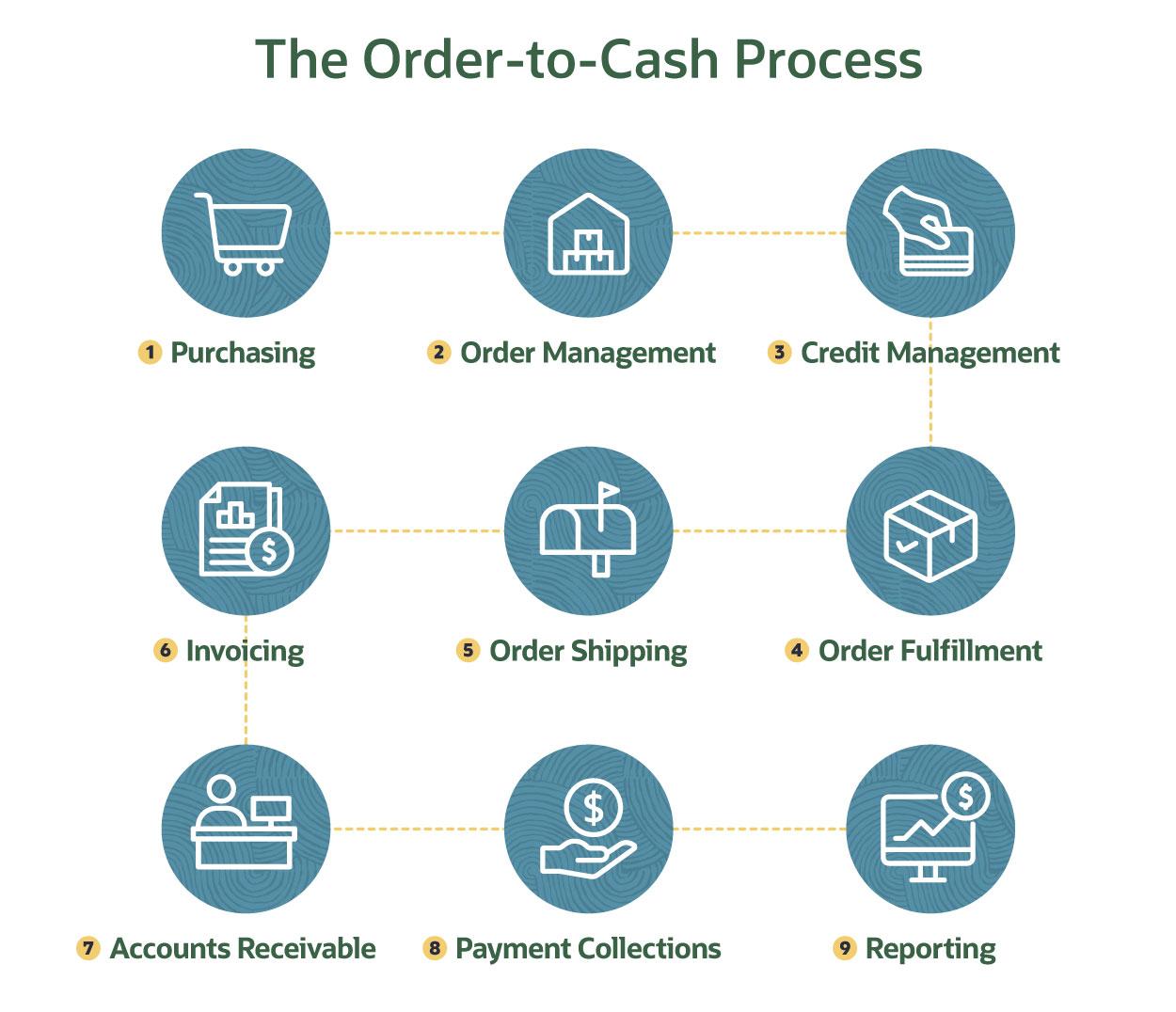
A typical O2C process includes these nine steps, which begin as soon as the customer places an order.
1. Customer Purchase
The purchasing process varies from simple online orders to complex sales that require a conversation with a sales associate and multiple internal approvals. Businesses must accurately capture all relevant information—from product specifications to delivery requirements—to initiate efficient order processing and fulfillment.
2. Order Management
Once the customer makes a purchase, order management moves the order through the rest of the order-to-cash cycle. Businesses can use order management systems to efficiently track the order at each stage, keep customers informed, and identify and resolve potential issues, such as out-of-stock items or shipping constraints, before they impact delivery times. Effective order management should also examine inventory levels before an order is placed to be sure an item isn’t temporarily out of stock or permanently unavailable.
3. Credit Management
If a business makes sales on credit, it’s important to continually assess customer financial risk. For new customers, businesses may run credit checks before extending credit payment terms. This step aims to limit losses by establishing appropriate credit limits and payment terms based on the customer’s financial history, as well as current financial and market conditions. With established customers, diligent attention to credit management and payment trends can help minimize the potential for overdue balances and bad debt write-offs.
4. Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is the process of picking and packing the ordered items and shipping them to the customer. This entails selecting the correct items from inventory—or manufacturing them, for built-to-order goods—assembling any custom configurations, and preparing everything for shipping. Coordinated warehouse management systems and clear interdepartmental communication can support accurate and timely delivery of ordered goods.
5. Order Shipping
Once the items have shipped, the customer should be notified and given an estimated arrival date. Shipping considerations can be complex and require expertise to choose the right shipping modes and find the best prices, especially for companies that sell internationally. Businesses may want to look into automated systems that can be used to generate tracking numbers, send customer notifications, and monitor delivery progress. For international shipping, businesses need to consider customs declarations and potential border delays when setting timelines.
6. Invoicing
Prompt invoicing helps accelerate the order-to-cash cycle and improves cash flow since customers can’t pay a bill until they receive one. So, it’s important to eliminate delays between fulfillment and invoice creation in order to get invoices into customers’ hands in a timely way. To speed up the invoicing process, supporting information including sales or purchase orders must be readily available to the invoice system. to the invoice system.
7. Accounts Receivable
Once the invoice is generated and sent to the customer, it’s up to the accounts receivable (AR) team to make sure payment is collected. Financial management software can help smooth the accounts receivable process by automatically tracking invoice due dates and sending reminders to customers. These systems can automate other processes as well, such as flagging overdue accounts and generating regular reports.
8. Payment Collections
It’s reality that not all customers pay on time. The AR team needs to accurately track which accounts are overdue and take action to collect payment when necessary. A delinquent customer’s account can also be flagged to prevent them from making further purchases. The sooner the payment collection process begins, the more likely the business will be able to recoup what customers owe. But because missed payments can result from simple oversights like incorrect billing addresses, forgetful customers, or outdated payment information, effective collection processes should carefully balance customer relationships with collecting timely payment.
9. Reporting
With the help of software, companies can analyze the efficiency of each stage in the order-to-cash cycle and identify areas for improvement. Integrated data management is critical for facilitating reporting and analysis. ERP software that integrates data from across the business and provides strong reporting capabilities can help the business track key metrics, such as total order cycle time and AR turnover ratio.
5 Order-to-Cash Best Practices
Improving the O2C process can improve cash flow by speeding up payments and can increase profit by reducing bad debts. Here are five best practices for enhancing your O2C cycle:
1. Analyze Each Step in the Process
Take a close look at how each step in the O2C cycle works. For example, after a customer places an order, is the order fulfillment process triggered automatically or does it require manual input? Are invoices sent automatically? What is the process for collecting past-due bills? The analysis should highlight areas where the process can be streamlined and automated.
2. Start With the Low-Hanging Fruit
Target areas where process improvements offer the highest return for the least effort. Common problem areas include fulfillment delays, high shipping costs, and late customer payments.
3. Automate
Automating the O2C cycle with software can help improve cash flow and operating efficiency while enhancing the ordering experience for customers. For example, software can improve AR processes by automating invoice generation and reconciliation, creating payment reminders, and flagging overdue accounts. Automation can also reduce errors in billing and order fulfillment by eliminating duplicate data entry.
4. Integrate Operations and Data With ERP
A smooth, efficient O2C cycle requires integration of data and operations across the business. That’s often difficult when companies use disparate software for each function. ERP software provides an integrated set of business applications that use a single unified database, helping businesses accelerate and automate the entire O2C cycle. Leading solutions also include advanced dashboards and reporting capabilities that help businesses monitor trends, quickly identify problems, and analyze process efficiency.
5. Listen to Customers and Staff
Your customers and your staff can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of your O2C process. If customers frequently complain about shipping delays or billing errors, it makes sense to prioritize those fixes. If warehouse staff can’t quickly find ordered inventory, it may be cost-effective to invest in a better inventory tracking and warehouse management system.
Order-to-Cash for Subscription Businesses
More businesses are turning to subscription models, from streaming media providers to monthly delivery services and software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies. Subscriptions can generate more reliable and predictable cash flows than the traditional models for selling products and services. However, they can also create complications for the O2C cycle. Billing can become much more complex, for example. Revenue recognition can also be challenging, particularly for companies that previously focused on product sales, as opposed to services.
Subscription services generally increase the volume of invoices because they require businesses to generate recurring bills at fixed intervals for the duration of the customer relationship. Adding to the challenge, the amount billed may vary from invoice to invoice. For instance, depending on a company’s business model and how subscription plans are structured, volume-based rates or overage charges can apply. Promotional discounts and free trials that eventually convert to full price subscriptions add to the billing challenge. Automating billing is essential, because preparing invoices manually for hundreds or thousands of customers every month makes it difficult to maintain accuracy, especially with complex pricing scenarios. Manual processes are also difficult to scale, meaning companies must continue adding accounting headcount as their business grows, which is unsustainable.
Order-to-Cash Process Challenges
Fixing a broken order-to-cash process can be hard, but it’s well worth the effort. These are some of the problems businesses face when they don’t fix common order-to-cash process challenges.
- Manual processing can be time-consuming: Processing orders, generating invoices, and reconciling payments by hand burdens staff and introduces opportunities for errors. Automated tools help staff complete these tasks quickly, reducing processing time and improving accuracy while freeing up time to focus on tasks such as managing customer relationships or pursuing new leads.
- Incorrect pricing information can lead to inaccuracies: When pricing data isn't consistent across systems, it leads to incorrect invoices, payment delays, and customer frustration. Centralized and integrated pricing tools, often built into larger ERP systems, allow businesses to automatically update information across all channels and create consistent pricing policies in every department.
- Delays may lead to dissatisfied customers: Slow order processing and delayed shipments can frustrate customers, damaging the business’s reputation and retention strategies. Incorporating real-time order tracking and automated notifications can minimize complaints by keeping customers informed at each step, even if delays occur.
- Potential for compliance or legal risks: Inadequate documentation and order inconsistencies can create regulatory compliance problems, particularly for international companies or those with strict reporting requirements. Noncompliance can lead to penalties, fines, legal action, reputational damage, or license revocation. Establishing standardized procedures during the O2C process and maintaining detailed digital records minimizes these risks and provides an audit trail to show compliance when needed.
Automating Order-to-Cash in ERP
Cumbersome, labor-intensive order-to-cash processes can cause problems for your business and for your customers. In addition to hurting cash flow, manual processes can cause problems such as shipping delays and inaccurate billing. NetSuite Enterprise Resource Planning enables businesses to streamline and accelerate the O2C cycle, improving cash flow by automating steps from order entry to fulfillment and payment. NetSuite ERP knits together the functions involved in the O2C cycle—sales, customer service, operations, accounting, and more—in a single integrated solution. NetSuite automates key financial processes, such as billing and revenue recognition, even for complex subscription-based pricing models. Businesses can monitor operating efficiency throughout the O2C cycle and identify bottlenecks using real-time dashboards and business intelligence tools.
A well-managed order-to-cash cycle is an important part of maintaining healthy business operations and strong customer relationships. When businesses prioritize improving their O2C processes, they can accelerate cash flow, reduce overdue invoices, and minimize the manual effort required from staff across departments. Faster deliveries, more accurate invoices, and transparent payment processes also tend to follow from a trusted order-to-cash process, enhancing the customer experience and supporting customer loyalty.
#1 Cloud
Accounting
Software
Order-to-Cash FAQs
What is P2P and O2C?
O2C stands for order-to-cash, the sequence of steps involved in processing customer orders. Sometimes abbreviated OTC, the O2C cycle starts with order placement and ends with the receipt of payment. P2P, on the other hand, stands for procure to pay and is the corresponding process businesses follow when purchasing, receiving, and paying for goods and services.
What is billing in order-to-cash?
In the order-to-cash process, the billing step involves requesting payment from a customer, typically by issuing an invoice.
What is order-to-cash process?
A typical order-to-cash (O2C) process includes nine steps, which begin as soon as the customer places an order. The steps include order management and fulfillment, invoicing, payment, and reporting.
What is job order costing?
Job order costing is a method that companies use for pricing and tracking the costs of custom products and services. It’s commonly used by companies that undertake complex one-off projects or make specialized products to meet a customer’s requirements.
What is the difference between order-to-cash and procure to pay?
While order-to-cash (O2C) manages how businesses receive and process customer orders and payments, procure-to-pay (P2P) handles the other side of business transactions: purchasing goods and services from suppliers. In other words, O2C focuses on selling goods and receiving payment, while P2P involves selecting suppliers, placing orders, receiving goods, and paying invoices.









